English can be one of the most challenging languages to learn, with its endless supply of confusing words. Whether you are just beginning to learn the language or have been speaking it for many years, some words are more difficult to understand than others. This blog post will look at some of the most confusing English words and explore their definitions and usages. So, if you’ve ever been left scratching your head and wondering what a word means, this post is for you!
Complement/Compliment
Complement and Compliment are two of the most confusing English words. While they may sound similar, they have different meanings and usage.
A complement is something that completes or adds to something else. Complements are usually used to describe a pair or group of items that work together to achieve something—for example, a suit, jacket and trousers or a pair of shoes. A compliment also adds or enhances something else, such as a garnish on a dish or a scarf to complete an outfit.
On the other hand, a compliment is an expression of admiration, appreciation, or respect. It’s a way of telling someone that you appreciate what they’ve done or how they look. For example, “Your new haircut looks fantastic!” or “You did an amazing job on that project.” Compliments are also a way of telling someone that you like something about them, such as “You have a great sense of humor.”

Defence/Defense
Regarding the most confusing English words, defense and defence are often at the top of the list. Defense and defence are two spellings of the same word, meaning the same thing, but they are used in different contexts.
Defence is the spelling used in British English, while defense is the spelling used in American English. These words are nouns that refer to protecting something from attack, harm, or danger.
When using these words in a sentence, it’s important to note that the meaning does not change with the spelling. For example: “The country has a strong defence against enemies.” and “The country has a strong defense against enemies.”
These words are also commonly used in legal contexts. For example, in criminal cases, lawyers and judges often refer to the defense or defense of a person accused of a crime. In civil cases, defence or defense may refer to a party’s attempt to protect themselves against a claim.
In sports, the terms defense and defence refer to the players and tactics used to prevent the other team from scoring. In football, for example, teams will have a defensive line and defensive backs, who are responsible for stopping the opposing team’s play.

Affect/Effect
Although Affect and Effect sound similar and have similar meanings, these words have different functions and cannot be used interchangeably.
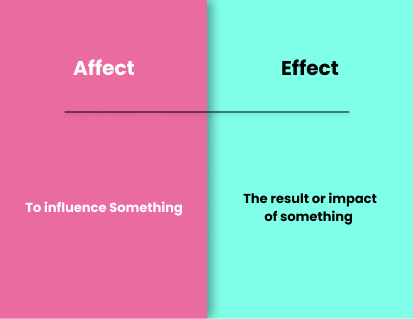
Affect is a verb and means to produce a change or influence something. For example, you can say, “The new policy will affect the employees” or “The bad weather will affect the crop yield.” In these sentences, affect means to cause a change or influence something.
On the other hand, the effect is a noun and means the result of an action. For example, you can say, “The new policy had a positive effect on the employees,” or “The bad weather had a negative effect on the crop yield.” In these sentences, effect means the result of an action.
To remember the difference between affect and effect, you can use the following mnemonic: “Affect (verb) acts on Effect (noun).”
Eminent/Imminent
Eminent and Imminent are commonly confused homophones, words that sound the same but have different meanings. The difference between the two words is subtle, but it can make a massive difference in the meaning of a sentence.
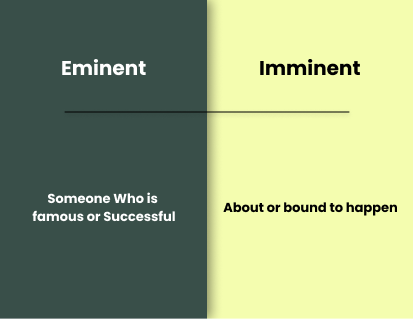
Eminent means “famous” or “distinguished.” It is often used to describe someone well-known or influential, such as a celebrity or a political leader. However, it can also be used to describe something that is of great importance. For example, one might say, “This painting is of eminent historical significance.”
On the other hand, Imminent refers to something that is about to happen or arrive very soon. It is usually used in the context of events and can have both positive and negative connotations. For example, we can say that an earthquake or war is imminent.
Flare/Flair
At first glance, flare and flair may appear to be identical. After all, they both refer to something that stands out or stands apart from the rest. However, there are subtle differences between these two words that are important to understand to use them correctly.
Flare is a noun that refers to a sudden, intense burst of activity or emotion. So, for example, if a person is experiencing an explosion of anger, we might say that the person is “in a flare of anger.”
On the other hand, flair is a noun that refers to a natural talent or aptitude for a particular activity. For example, a person may have “a flair for painting” or “a flair for organizing.”

Loose/Lose
“Loose” and “Lose” are pronounced the same, except for a subtle difference in the “o” sound. Many English learners find it difficult to distinguish between these two confusing words.
Loose is an adjective that means not firmly attached or held in place. It can also mean “not tight or confined” or “free from restraint.” So, for example, you can say, “the screw is loose,” or “the prisoner escaped from his loose handcuffs.”
On the other hand, lose is a verb that means “to suffer a loss or fail to keep or maintain.” So, for example, you can say, “I lost my wallet,” or “I’m afraid I’ll lose my job if I don’t improve my performance.”

To/Too
To and too are two of the most confusing small words, as they sound almost identical, so it’s no wonder so many people struggle to remember when to use which one.
“To” is a preposition describing a relationship between two things. It is used to express movement, direction, or purpose. For example, “I went to the store” means that the speaker moved from their current location to the store. Another example is, “I gave the book to him,” which means you gave the book to the other person.
On the other hand, “too” is an adverb that is used to indicate an excessive amount. It suggests that something is more than what is acceptable or necessary. For instance, “He was too lazy to do his homework” means that he was too lazy for the situation. Another example is, “She was too nervous about speaking,” which suggests that nervousness was too much for her to speak.

Lead/Led
Lead is the present-tense verb form of the word and is used to describe an action that is currently taking place. It is used to describe the act of guiding, directing, or influencing someone or something. For example, you can say, “She is leading the team,” to mean that she is currently guiding or directing the team.
Led is the past-tense verb form of the word and is used to describe an action that has already taken place. It is used to describe the action of guiding, directing, or influencing someone or something in the past. For example, you can say “She led the team” to mean that she guided or directed the team in the past.

Breath/Breathe
Breath is a noun and means the air that is inhaled and exhaled during respiration. For example, you can use the phrase “She took a deep breath” to describe how someone inhales a deep breath of air.
On the other hand, breath is a verb and describes the act of inhaling and exhaling air. So, for example, you can use the phrase “She was breathing heavily” to describe someone inhaling and exhaling with effort.
It is important to note that breath and breathe cannot be substituted for one another in any context. It would help if you used the correct word to convey your meaning accurately.

Perquisite/Prerequisite
Perquisites and prerequisites are similar concepts, but they differ in their usage and definition.
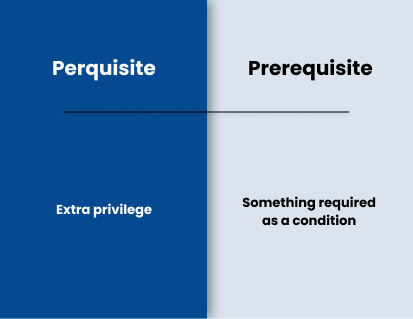
Perquisites are privileges or benefits that are given to someone in addition to their salary or wages. They are not legally required, nor are they dependent on particular qualifications or job performance. Examples of perquisites include company cars, bonus payments, or exclusive access to events.
Prerequisites, however, are the conditions that must be met for someone to be eligible for or pursue something. Prerequisites can be educational, such as the required courses for a degree program, or professional, such as the years of experience needed for a job.
Anyway/Any way
The words “anyway” and “any way” are two very different words that are often confusing and misused. Knowing these two terms’ differences can help you choose the right word for the situation.
“Anyway” is an adverb that means “in any case” or “regardless.” For example: “I don’t understand why you did that, but anyway, let’s move on.” In this sentence, “anyway” expresses the idea that we should move on from the situation regardless of why it happened.
“Any way” is a phrase that means “in some manner or another” or “in any fashion.” For example: “There must be anyway we can make this work.” Here, “any way” indicates that there could be a solution to the problem, no matter how unlikely it may seem.

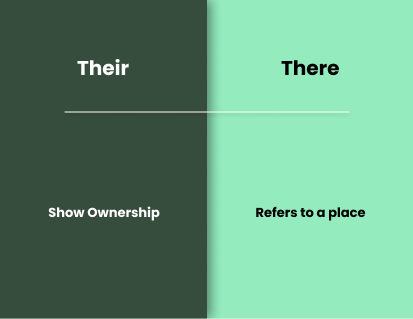
Their/There
One of the most commonly confusing words is “Their” and “There.” What is the difference between these two? In what situation can you use them?
“Their” is a possessive pronoun. It is used to show possession or belonging to a group of people or things. For example, “Their books are on the table.” This sentence implies that the books belong to a group of people.
“There” is an adverb. It is used to indicate the existence of a place, person, or thing. For example, “There is a cat in the garden.” This sentence implies that the cat is in the garden.
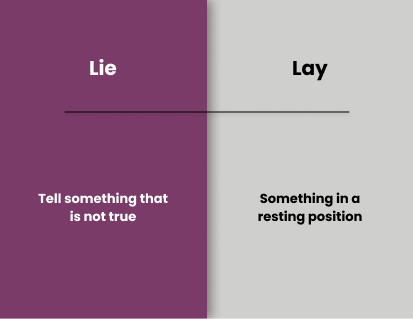
Lie/Lay
Lie and lay are two commonly confused words in the English language. While they have similar pronunciations and similar spellings, they have very different meanings and uses.
Lie is a verb that means to recline or to be in a horizontal position. It can also mean to tell an untruth or to be in a state of false belief. For example, if you are lying on the couch, you are reclining in a horizontal position. If you are lying to your friend, you are telling an untruth.
Lay is also a verb, but it has a different meaning. Lay means to place or to put something down. For example, if you are laying books on a table, you are placing them on the table.
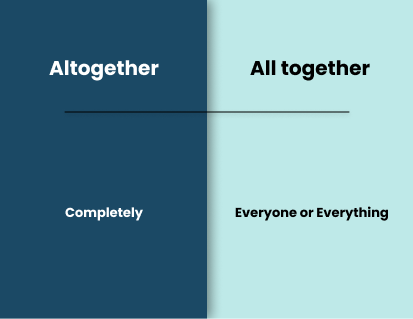
Altogether/All together
Altogether and all together are two phrases that are often used interchangeably, but there is a subtle difference in the meaning of these two phrases.
Altogether is an adverb that means “completely” or “entirely.” It is typically used when talking about a group of people or things considered a whole. For example, you could say, “We are altogether in agreement.” This means that everyone in the group agrees on the topic.
On the other hand, all together is a phrase that means “in one place or a group.” It is often used to describe physical proximity, but it can also be used metaphorically to describe a situation in which everyone agrees. For example, you could say, “We are all together in our decision.” This means that everyone in the group has come to the same decision.
Advice/Advise
Advice is a noun and a recommendation about what someone should do. An example of advice is, “I suggest you take some time off work to relax.”
Advise, on the other hand, is a verb, and it is to give someone advice or to recommend a course of action. An example of advise is, “I advise you to take some time off from work to relax.”

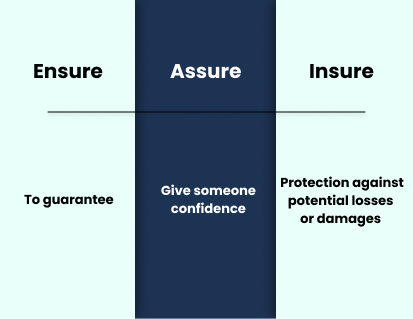
ensure/assure/insure
It can be challenging to keep them straight when understanding the differences between ensure, assure, and insure.
Ensure means to make sure that something is done or that a situation is achieved. It is often used interchangeably with guarantee but is less absolute. For example, you might say, “I will ensure that the job is completed on time.”
Assure is a term used to express certainty or to guarantee something. It is often used to express confidence in someone or something. For example, you might say, “I assure you the job will be completed on time.”
Insure is a term used to describe any form of insurance. It is typically used for financial protection against potential losses or damages. For example, you might say, “I will insure my car against theft and accident damages.”
Access/Excess
Access is related to the ability to use something. It can refer to the ability to reach a particular resource or person or to use a particular service. For example, a library might have access to certain books that other libraries do not. Access can also refer to the ability to use technology, such as a computer or internet connection.
Excess is related to having more than is necessary or desirable. It can refer to having too much of something. For example, a person may have excess money, meaning they have more than they need. It can also refer to having too much of something undesirable, such as excess clutter in a home.
In some cases, access and excess can be used together. For example, a person may have access to a lot of money but still have an excess of it, meaning they have more than they need. Similarly, a person may have access to a lot of clutter but have an excess of it, meaning they have more than they need.

Currant/Current
The word ‘currant’ refers to a small, sweet-tasting, seedless grape. It is a member of the Ribes family, including grapes and currants. Currants are typically dried and used in baking, jams, jellies, and other dishes.
On the other hand, current refers to something that is up-to-date and happening now. For example, someone might say, “This current news story is making headlines worldwide.” Here, current indicates that the news is timely and relevant.
Envelop/Envelope
An envelop is a cloth or paper wrapper used to cover and protect more essential items. Common examples of items wrapped in an envelop include books, magazines, and large documents. An envelop is typically made of cloth or heavy paper and is often sealed with a string, ribbon, or secure closure.
On the other hand, an envelope is a paper container with a flap on one side used to enclose a letter. The envelope is intended to protect the contents of the letter and is commonly made of paper, paperboard, plastic, or a combination of the three. A postal worker will use an envelope to send letters, documents, and other items through the mail.
Liable/Libel
Libel is a false written or published statement that harms the reputation of an individual or organization. It is considered to be a form of defamation. It is defined as a “maliciously false and unprivileged publication by writing, printing, picture, effigy, or other fixed representation to the eye, which exposes any person to hatred, contempt, ridicule, or obloquy, or which causes him to be shunned or avoided, or which has a tendency to injure him in his occupation.”
On the other hand, liable is a legal term to describe someone responsible for a debt or obligation. This can be a person, business, or any other entity legally required to pay a certain amount or fulfill a specific obligation.
For example, if an individual is sued for a debt or a breach of contract, they may be held liable for the debt or the obligation. Similarly, if an individual is sued for damages caused by accident, they may be found liable for the damages.
Peace/Piece
Peace is a state of tranquility, harmony, and goodwill without conflict. It’s often used in the phrase “peace and quiet” to describe a pleasant atmosphere or to refer to a state of freedom from war or violence. For example, you could say, “The town was filled with peace and quiet.”
The piece, on the other hand, refers to an individual item or part of something. It’s often used in the phrase “piece of cake” to describe something easy to do. For example, you could say, “Cleaning the house was a piece of cake.” It can also refer to a single item or part of a more extensive collection, such as a “piece of furniture” or a “piece of jewelry.”

Personal/Personnel
As a business owner, it’s essential to understand the difference between personal and personnel. These terms are often used interchangeably, but they do have distinct meanings.
Personal refers to a single individual or a group of individuals in a personal context. This includes people, their relationships, and their possessions. For instance, when discussing personal matters, you might refer to a person’s family, friends, hobbies, or interests.
Personnel, on the other hand, refers to the staff or employees of a business. It includes their roles, duties, and responsibilities. Their qualifications and experience are also considered part of the personnel. Therefore, when discussing personnel, you are likely referring to a department or team of people.
Role/Roll
A role is a part or character that someone plays in a situation, whether in real life or a fictional story. A role can be assigned to someone, or a person can take on it to play that character. For example, if you’re in a play, you will be assigned a role, such as the lead actor or singer. On the other hand, if you’re in a group of friends and you decide to be the group’s leader, you have taken on a role.
On the other hand, a roll is a verb used to describe the motion of an object. It can also describe the movement of someone or something in a specific direction. For example, you can roll a ball across the room or a wheelbarrow down a hill. It is important to note that a roll is not used to describe the motion of a person or animal, as that would be walking or running.
Stationary/Stationery
Stationary describes stationary objects or items that are not meant to be moved. For example, a desk can be described as a stationary object, while a chair is considered a mobile object. Similarly, a stationary bike is a bike that does not move, while a regular bike moves along the ground.
Stationery is often used for writing letters, creating cards, or sending notes. Stationary is used to create a comfortable and inviting atmosphere. Sofas, armchairs, tables, and other furniture are all considered stationary items. Stationery is also commonly used for creating invitations, thank-you notes, and other documents.
Principal/Principle
Principal and Principle are two words that often need clarification. While they are spelled similarly and sound alike when spoken, they have very different meanings.
The principal is an adjective that means “first in rank or importance” or “chief or main.” For example, an individual may be referred to as a company’s “principal shareholder” or the “principal owner” of a business. It can also describe a school’s head administrator: the principal.
The Principle has two meanings. It can refer to a fundamental truth or law, or it can refer to a moral code. For example, “Honesty is a principle that should be upheld in all circumstances” or “The principle of gravity explains why objects fall to the ground.”
Pray/Prey
When you pray, you ask for something from a higher power with gratitude and humility. Prayer is often seen in religious contexts, such as when someone asks for a blessing or guidance. It can also be used in secular contexts, such as when someone asks for strength or courage to face a challenge. Praying can be done in solitude or a group, and it can take many forms, including spoken words, silent prayers, and meditation.
On the other hand, when you prey, you are hunting or capturing animals for food or sport. Prey is usually associated with predatory animals, such as lions or wolves, but it can also describe humans who hunt for pleasure or profit. Prey does not have the same spiritual or moral connotations as prayer; instead, it’s focused on physical action or aggression.

Desert/Dessert
Desert is a noun that refers to a barren area with little or no vegetation, usually covered in sand. It is an arid landscape with very little rainfall, often described as a “wasteland.” Examples of deserts include the Sahara in Africa, the Gobi in Asia, and the Sonoran in North America.
On the other hand, dessert is a noun that refers to a sweet course or dish served after the main course at the end of a meal. It is derived from the French word ‘desservir,’ which means “to clear the table.” Examples of desserts include cake, ice cream, pudding, and cookies.

Farther/Further
Farther is used to refer to physical distance. This could be a literal distance (e.g., from one place to another) or a figurative distance (e.g., from one point in time to another). For example, you might say, “We drove farther than we expected.” In this sentence, “farther” refers to a distance greater than expected.
Further is used to refer to figurative or abstract distance. This could include a figurative distance in a conversation, a figurative distance from one point of view to another, or a figurative distance in the development of an idea. For example, you might say, “Let’s look further into this issue.” In this sentence, “further” refers to an abstract distance or a more in-depth exploration of the issue.
Forth/Fourth
The word ‘Forth’ means onward or forward. It is often used to indicate progress or movement. For example, you might say, “We are moving forth on our project.” It can also indicate the progression of time, such as in the phrase “a month henceforth.”
On the other hand, ‘Fourth’ is a number, precisely the number four. It is used to indicate a specific order or placement. For example, you might say, “This is the fourth time I’ve been to this place.” It can also be used to refer to a specific date on the calendar, such as the fourth of July.

Pole/Poll
Pole is a noun that refers to a long, thin object made of metal, wood, or plastic that is used to support or carry something. For instance, a pole can hold up a tent, hang up a banner, or hold up a flag. Poles are also used in sports like skiing, pole vault, and pole dancing.
Poll is a verb that means to ask a group of people for their opinions on a particular topic. Polls are often used to gauge public opinion to make decisions about policy or to gauge the popularity of something. For example, a politician might conduct a poll to see how people feel about a particular topic, or a company might poll to see what products people are most interested in.
To Sum Up
Overall, the most confusing English words are essential to know and understand to improve your English language speaking skills. Using online language polishing apps can be beneficial in helping you to refine your English and become a more proficient speaker. With practice, dedication and patience, you can become more confident in your ability to use English in various settings.